Abstract
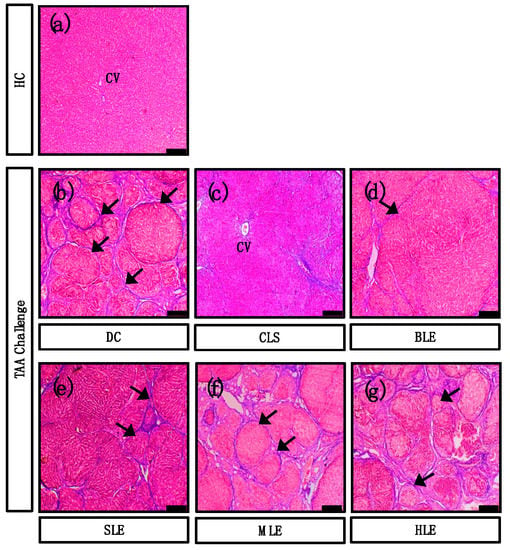
Chronic liver inflammation has become a major global health concern. In the absence of clinical surrogate markers to diagnose inflammatory liver disease, the intervention with effective drugs in modern medicine tends to be late. In Sri Lanka, traditional medical practitioners prescribe herbal preparations from Osbeckia octandra for the prevention and treatment of liver disorders. To test the efficacy of such treatments, we have administered thioacetamide (TAA) to male Wistar rats to induce chronic liver damage (disease control; DC) and examined how various leaf extracts: crude leaf suspension (CLS), boiled leaf extract (BLE), sonicated leaf extract (SLE), methanol leaf extract (MLE) and hexane leaf extract (HLE) of O. octandra ameliorate TAA-induced liver disease. The CLS, BLE and SLE treatments in cirrhotic rats significantly attenuated disease-related changes, such as liver weight and hepato-enzymes. The mRNA levels of Tnf-α were significantly decreased by 3.6, 10 and 3.9 times in CLS, BLE and SLE compared to DC. The same treatments resulted in significantly lower (19.5, 4.2 and 2.4 times) α-Sma levels compared to DC. In addition, Tgf-β1 and Vegf-R2 mRNA expressions were significantly lower with the treatments. Moreover, BLE expressed a strong anti-angiogenic effect. We conclude that CLS, BLE and SLE from O. octandra have potent hepatic anti-fibrotic effects in TAA-induced liver cirrhosis. View Full-Text
View Full-Text https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164836